Blog

Lockdown Stories: Taking on New Challenges and Supporting Local Causes
Like a lot of companies, SL Controls had to pivot quickly when the first lockdown was introduced in March of this year. The restrictions since then have varied as the country battles the Covid-19 pandemic, but life and work for SL Controls employees remains very different from what it used to be.
We spoke to members of the team to find out more about what they did during the lockdown and how it affected them.
Vinnie Boyd, Business Development Associate
 “During the lockdown, I thought I’d do something ridiculous like running 10k a day for the month of May. I had the time and I wanted to keep active, plus I thought it would be an opportunity to raise money for charity.
“During the lockdown, I thought I’d do something ridiculous like running 10k a day for the month of May. I had the time and I wanted to keep active, plus I thought it would be an opportunity to raise money for charity.
“I am involved with Shamrock Gaels here in the Riverstown/Castlebaldwin/Sooey area. One of our former players and club members, John Lyons, sadly died earlier in the year in March. He was heavily involved with the club, and his wife and children continue to be involved. So, I and a couple of the other guys from the club thought it would be a good opportunity to set up an event in memory of John and to raise money for North West Hospice.
“We talked to the club and decided to change it from 10k a day to a more realistic 5k a day. We then basically reached out on social media, mostly on Facebook. We got loads of video messages from people like international rugby star and former international basketball and Shamrock Gaels player, Aoife McDermott, Kerry’s All-Ireland winner Stephen O’Brien, Tyrone manager Mickey Harte, Ireland captain Seamus Coleman, Mayo’s Lee Keegan, and legendary commentator Micheal O’ Muircheartaigh.
“Slaughtneil and Derry captain Chrissy McKaigue, Tipperary GAA ladies star Aisling Moloney, Dublin’s six-time All-Ireland winner Jonny Cooper, and former Irish rugby international Tommy Bowe were some of the other people that left us messages. The support really was amazing, and it certainly kept everyone motivated throughout the month.

“In the end, 150 people from the GAA club, the local community, and beyond signed up to take part. Some walked and some ran the 5k a day then, at the end of May, we finished with a relay from the late John Lyons’ house to the Shamrock Gaels pitch. In total, the participants covered well over 20,000 km.
“When we started out, we thought the event would raise a few thousand, but, in the end, we raised almost €29k.”
Deirdre Loughlin, Quality & Marketing Executive
 “Before the lockdown, my day would have involved getting up early to go to the gym before work. All the gyms had to close during the lockdown, so I decided I would get back into running.
“Before the lockdown, my day would have involved getting up early to go to the gym before work. All the gyms had to close during the lockdown, so I decided I would get back into running.
“Running is something I had been trying to get more into for about two years, but I ended up concentrating more on the gym. There was no choice during the lockdown, so I decided to get up to a level where I could run 5k.
“I found an app to help me achieve that – Pop Up Races. It lets you enter challenges where you support charities while you are running. It really gives you a reason to run, especially on those days where you maybe don’t feel up to it. Knowing you are supporting a charity gives you that extra push to do it.
“You also get a medal for some of the challenges when you finish, which is always nice to receive.
“This led to me also doing other virtual events, including the Virtual Warriors Run which usually starts at Strandhill beachfront to the top of Knocknarea mountain and back to the beachfront. This year, it was 15k your way, which you could complete in stages anywhere in the world while raising money for Focus Ireland.


“So, part of the lockdown experience for me involved competing in events I would have never done before – all virtually, of course. It’s nice to support charities, too, as they are getting hit very badly during these times.
“I’m looking forward to getting back into the gym when things return to normal, but I plan to continue with the running too.”
Shane McLaughlin, Business Development Manager
 “For me, working remotely is a familiar experience. For about the last four years, my week would have been working about three days on the road and the rest from the house. So, from a work perspective, the lockdown was not a massive change for me.
“For me, working remotely is a familiar experience. For about the last four years, my week would have been working about three days on the road and the rest from the house. So, from a work perspective, the lockdown was not a massive change for me.
“The way we do things is different. There is less travel now, and where before I would have interacted with a lot more people face to face, now we meet through Microsoft Teams. But everybody is in the same boat.
“There are a lot of positives to take from the experience too. Personally, I used the time to take on new challenges. This included walking and running 100k in 30 days for Cancer Ireland, which we did together as a family between Teams calls and everything else.
“A challenge for frontline heroes was another one I got involved with, but the big one was a virtual Mizen Head to Malin Head where you run 600k over six months. I got through that by doing short runs during the week and a longer run at the weekend.

“I also joined Tullamore Harriers running club recently and have taken part in runs. It’s good because I ran a bit before the lockdown, but it is more consistent now. The kids come with me sometimes too, cycling beside me while I’m running.
“I’ve also been involved with Tullamore Triathlon Club for a few years. This year we did a virtual Iron Man, covering the equivalent of an Iron Man event over 10 days. There haven’t been any races this year because of Covid, but it was good to see people getting involved in the socially distanced virtual events that did happen.”

Too Much Too Soon – Avoiding Factory Automation & Smart Factory Implementation Risks
The smart factory and digital manufacturing technologies are the future of manufacturing. That said, change in business carries risks, particularly when those changes involve creating fundamentally different business and manufacturing processes. Smart factory technologies are not immune to such risks.
One of the clearest examples of how the smart factory can go wrong comes from Tesla and the early days of production of its Model 3 electric car. While production processes have significantly improved at Tesla, those early days provide valuable lessons on implementing smart factory solutions.
Descent into Hell
Tesla – and specifically its innovative CEO Elon Musk – made much of its fully automated production lines when it was introducing the much-anticipated mid-size all-electric car, the Model 3. The ultimate goal was that robots would completely take the place of humans in “alien dreadnought” factories to manufacture the Model 3 and other cars.
Tesla even bought a company that specialises in automated manufacturing to accelerate its vision for a fully robotic production line.
It didn’t take long, however, for problems to occur, most evidently in missed production targets in those early days. At the end of 2017, Musk described manufacturing the Model 3 as “production hell”. This was at a time when he was sleeping in the company’s conference room so he could work all-nighters trying to fix the problem.
Musk eventually wrote in a Tweet: “Yes, excessive automation at Tesla was a mistake. To be precise, my mistake. Humans are underrated.”
Fast-forward to today, and the position of the Tesla Model 3 and the company’s manufacturing processes are much transformed. Musk and the Tesla team continue pushing the boundaries of innovation in areas like digital manufacturing, production processes, and automation.
They are building prefabricated factories in a fraction of the time it would normally take to build a factory, and they are manufacturing at an impressive scale. For example, a manufacturing plant that Tesla bought in 2010 from GM and Toyota is thought to now have a production capacity of around 400,000 cars a year, up from just 10,000.
What, however, can be learned from the early mistakes and challenges that Tesla faced in its forceful early push into smart factory and digital manufacturing technologies? One of the most significant is the importance of building a value proposition.
Building a Value Proposition for the Smart Factory
When considering smart factory technologies and how you can implement them on your production lines, the first step you should take is to build a value proposition. This is the only way you will fully understand the impact that digital manufacturing and related Industry 4.0 technologies will have on your business.
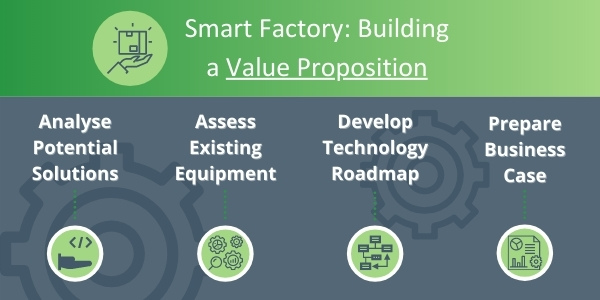
Building this value proposition involves several steps:
- Properly analysing potential solutions applicable to your plants.
- Assessing the current digital maturity of your equipment and systems.
- Developing a technology roadmap.
- Preparing a business case that includes expected productivity gains and efficiency savings as well as risk assessments, analysis of the impact of the new technologies on other parts of your business, how you should measure results, recommended next steps, potential opportunities, and more.
It is also good to understand the difference between “leading edge” and “bleeding edge” technologies. These two terms provide an important distinction to a broad group of technologies often described as “cutting edge”.
Bleeding-edge technologies are cutting edge, but they are also so new they have yet to be proven. Avoiding bleeding edge technologies is almost always the best approach.
Leading-edge technologies are also cutting edge, but they already have a proven track record of success. These are the technologies you should focus on.
Walk Before You Run
It’s an old cliché but walk before you run is apt when it comes to smart factory and digital manufacturing technologies. In other words, you should never implement a smart factory solution for the sake of the smart factory. You shouldn’t do it because it is the cool new tech either, or because there is a perception that your competitors are doing it.
Instead, you should explore smart factory solutions in the context of improving your business. The starting point, therefore, should be understanding what those improvements will be. You can then make an informed decision on what’s best for your business.

Company, Team, Family: The Lockdown Experience for SL Controls CEO Keith Moran
Everyone’s experience of living and working during lockdown will have been different, but there are a lot of similarities, too. Many of us are now working differently than we ever did before. Re-evaluating how we use our time is another common theme having lived through the spring/summer lockdown, as is looking again at our work-life balance.
For SL Controls CEO Keith Moran, the above rings true.
Then there is the added element of navigating a company through a changing operational environment while also managing a team going through their own lockdown experience, developing various scenario plans, and delivering on client requirements and expectations in industries – pharmaceutical and MedTech – facing their own challenges and expectations as part of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Lockdown & the Company
“Initially, when we went into lockdown, I think we all thought it would be for a month or so,” said Keith. “We certainly didn’t envisage it lasting, in whatever form, for seven-plus months and counting.
“The lockdown wasn’t as daunting for SL Controls as it might have been as we already had the required infrastructure in place. We invested in Microsoft Teams and other technical solutions a long time ago, and we have experience of our people working in virtual teams.
“Like most people, I didn’t see this situation coming, but, as a company, we were well prepared. We could continue operating efficiently, moving the business forward.”
One thing Keith and the management team didn’t know, however, was how SL Controls’ clients would react to the lockdown.
Keith said: “That was an unknown, but the professionalism of our clients was world-class. At the beginning, they took a step back, assessed the situation, looked at the risks, and analysed their priorities.
“They then put in place processes and structures that enabled them to bring people back safely.
“So, at SL Controls, we remain as busy as ever, continuing to deliver on existing client projects while also starting new projects to meet immediate needs as well as to help deliver on Industry 4.0 roadmaps and objectives.”
Lockdown & the Team
As part of a new internal strategy launched at the start of the year, Keith made a commitment to staff to post regular video updates about what was going on in the company.
Keith said: “The lockdown gave me the impetus to send video updates to the team, not just emails.
“In the videos, I tried to include an overview of my day and what it was like working at home, my wife working at home, and the kids being at home. I wanted to normalise the changed reality: juggling work, schoolwork, taking breaks, going out to play football at 11 in the morning.
“It was about getting the message across that we are all juggling the best we can. We knew some people would find it hard, some were worried about childminding, and there were other concerns.
“I wanted everyone to know the company would support them every step of the way. And I wanted people to know that just because I am the CEO, I am no different to anyone else.”
At the start of the lockdown and then more recently, SL Controls surveyed the team to get views on the lockdown and how people felt about how they work. A second survey was conducted more recently that showed the majority of people liked the idea of working from home for part of the week.
So, the company is finalising plans for accommodating those requests and are looking at changing the way the business operates with fewer people in the office. As always, the pace at which these plans will be implemented will depend on the restrictions and recommendations from the Government and health authorities.
Of course, being part of a company is not just work as there is a considerable social aspect, too.
Keith said: “We’ve looked at inventive ways to keep the social interactions outside of work going even though we can’t go anywhere in person. We’ve done a step challenge, people have been involved in virtual poker nights, and we’re going to do an online quiz. It’s about bringing people together for a bit of a laugh.”
Lockdown & Family
Keith said: “My day-to-day experience before the lockdown typically involved spending a lot of time in the car going to meetings across the country. I often wasn’t home until after the kids went to bed, and I was always tired when I got home. I was sometimes able to do school runs, but not often, and the weekends were short.
“So, the lockdown was a huge change for me, and it was only when I stopped and took a step back that I released what I was doing.
“Working from home, it was amazing the difference in how I felt in terms of energy. I looked healthier, I wasn’t tired, I wasn’t stressed out, and I wasn’t as cranky at home – at least, I think I wasn’t!
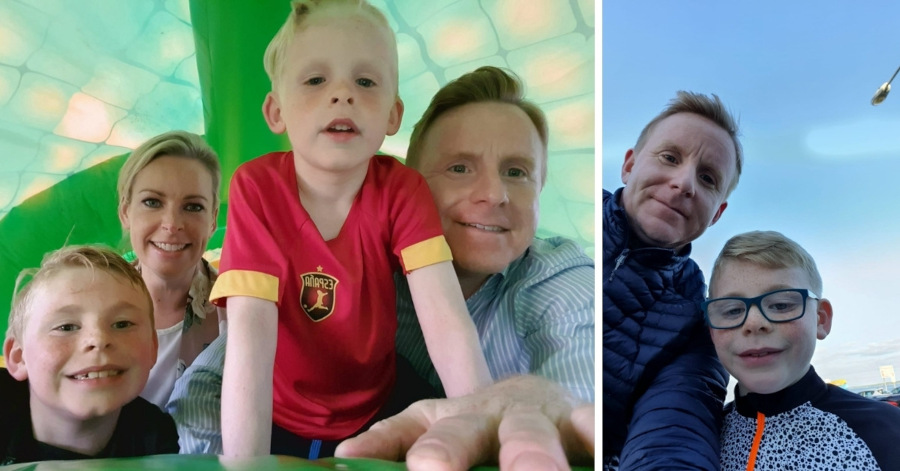

“I was spending more time with kids, too. And it was quality time. They were at home doing their schoolwork, so we’d all take breaks together halfway through the morning to play football.
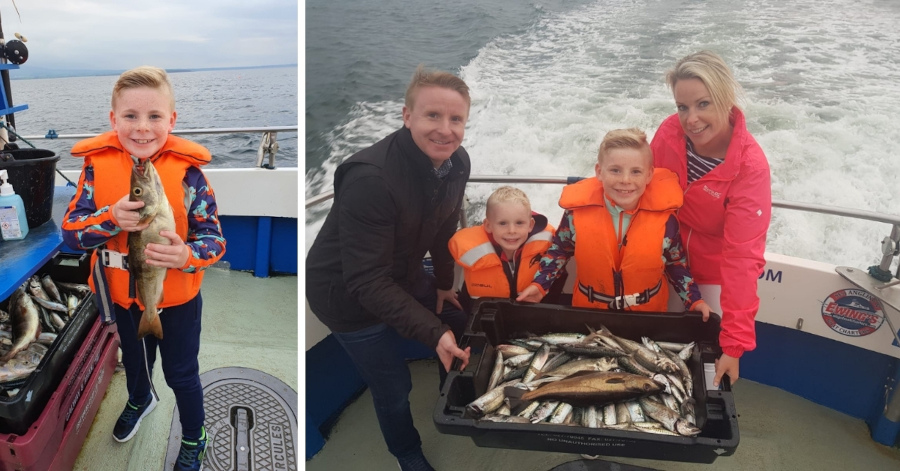
“We’ve become closer, and we got to do things we’ve never done before. My boys always wanted to go fishing, so we rented a boat and went sea fishing, and they caught their first fish!

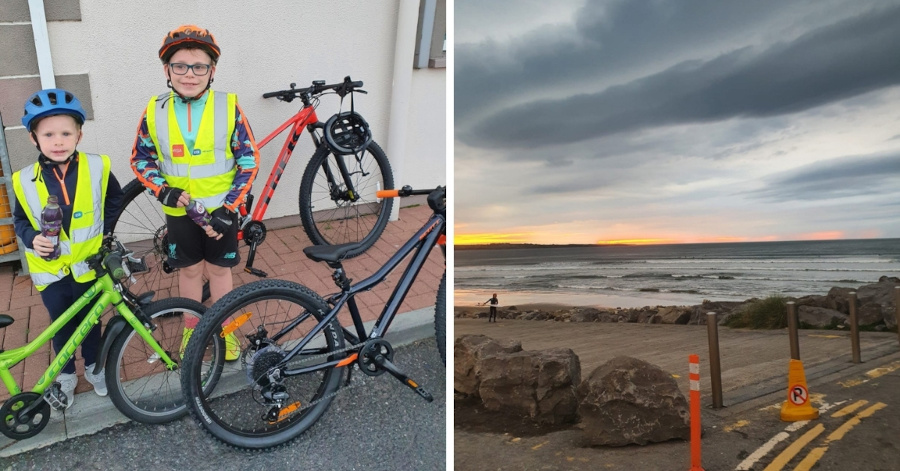
“We also bought two new bikes and started cycling a lot.
“I was able to spend time bonding with the kids, being there for them, and doing stuff.

“I also used to pick up colds and stomach bugs a lot, travelling so much and burning the candle at both ends. But I haven’t been sick at all this year.
“I was able to deal with some injuries, too. I play a lot of squash, but as I’ve got older, the injuries have started to creep in. A personal trainer I know told me I needed to do strength and conditioning work, but I never had the time.
“During lockdown, that changed. He started giving online strength and conditioning classes. So, I bought some weights, and me and a group of the guys from the squash club signed up for the classes. Where I didn’t have time before, those one-hour classes have seen my fitness levels and injuries improve.”
Overall
So, how does Keith sum up his lockdown experience?
He said: “It allowed me to re-evaluate. At SL Controls, we re-evaluated many aspects of our operations and continue to do so. Personally, the lockdown allowed me to re-evaluate what I was doing with my time, how efficient I was, the bonding experience with my family.
“For me, and I think for many people, the lockdown forced this re-evaluation on us, but we now realise the benefits.”
Case Study: Performance Monitoring of Databases in High-Volume Production Facilities
Manufacturing in all sectors is increasingly becoming data driven. Part of this shift to data is the use of databases for parts tracking on a production line, rather than the more traditional PLC shift register approach.
With a database managing the movement of data, individual machines on the line can operate independently, processing multiple lots simultaneously in a controlled manner.
Using this process, when a new part is loaded to a machine, the machine reads the part information from the database. This information includes previous process values alongside the part’s status. The machine can then determine whether to process the part or, if it was previously deemed a failure, not process it. If the machine does process the part, it will write back new part data and an updated status once its operations are complete.
This approach delivers substantial productivity gains as machines can produce lots independently of other machines on the line.
However, problems can arise when you look to scale a parts tracking database.
One of our customers faced this precise issue. The customer, a manufacturer in the life sciences sector, had developed their own part tracking database to move data between a large number of machines. This database operated effectively, but new plans for the line involved the acquisition of 50+ new machines.
How could the customer verify their database was fit for this new production capacity? Would the database be able to perform at the scaled-up level?
Objectives
The customer engaged us at SL Controls to develop a solution that would give them the answers they needed to confidently move forward with enhancing their production capacity. The solution needed to fully scale and test interactions with the database at the enhanced level, ahead of the arrival of the new machines.
What We Did
The SL Controls team quickly dismissed one potential solution – the setting up of 50+ PLCs to run the required tests. This approach was too costly, it would take up too much space, and it would take too long.
So, we started to investigate existing database loader tools that enable the fast bulk uploading of data. There are a number of solutions available on the market, many with impressive features. However, they all lacked flexibility, only allowing you to insert either fixed data or randomised data at predefined levels.
This rigidity made the existing database loaders unsuitable because of the complexity of our customer’s part tracking database. Foreign key constraints when inserting data was also an issue.
Instead, we needed a solution that would allow us more flexibility when constructing interactions.
We decided the best approach was to develop a customised database loader tool that could facilitate all the requirements of the project and emulate all critical machines on the line.
Our new and fully customised SL DB Loader tool replicated seven different machine variations. It could also trigger four different database operations.
Each machine emulation had four key features:
- A dedicated session to an Oracle database server
- A configurable period for database interactions, both inserts and queries
- A configurable number of rows that could be inserted into the predetermined tables
- The ability to log database interaction times for analysis
Results
The SL DB Loader tool allowed our customer to emulate the production environment with the additional machines before any of those machines arrived at the facility.
This enabled their database analysers to identify performance gaps. They were then able to use this knowledge to create solutions and countermeasures to ensure the database would be available to all machines at the enhanced level of production.
As a result, the customer had the verification data required to proceed with the acquisition and introduction of the new machines.
The solution went a stage further, too, as they were also able to use the SL DB Loader tool to understand how future machine performance improvements would impact the database.
To find out more about this project as well as how we can help develop data solutions for your production facility, please get in touch with us at SL Controls today.

Taking an Agile Approach to Talent Management to Meet Client Requirements
The needs of the high-volume manufacturing sector are rapidly changing, particularly in highly regulated industries. If you are in a leadership role in one of these industries, you need solution providers who can respond quickly to your requirements to ensure you remain competitive while also maintaining accuracy, quality, and compliance.
This requires a new approach to talent management, something which is especially important for service providers delivering Industry 4.0 solutions where the pace of change, scale of risk, and size of opportunity are all significant.
For us at SL Controls, we have adopted an agile approach to talent management to respond to the changing needs of clients, react to market conditions, manage the evolving requirements of regulators, and more.
The Agile Approach to Talent Management
We are a tech company, so we have extensive experience in the agile approach to developing software and technology solutions.
While you can’t export the entire tech agile approach to the talent management function of a business, you can adopt the same principles.
The goal is to strip away restrictive, bureaucratic, and rules-based processes, replacing them with simpler, faster, and more flexible models capable of responding to change.
This makes it possible to deal with rapidly evolving client needs, even at short notice.
Transforming Talent Management
The top-down, climbing-the-corporate-ladder approach has long been consigned to the history books, particularly in modern and rapidly growing companies. Only now, however, are we seeing a truly transformative approach to talent management in sectors like manufacturing where talent-related principles and processes are changing.
SL Controls is at the forefront of these changes in our industry and our field of equipment systems integration.
Our talent management function is comprehensive and detailed. Still, there are some significant differences we can highlight between the agile approach we have adopted and the more traditional way of managing a team.
Mix of Both Employees and Contractors
At SL Controls, we believe the right approach to delivering client expectations is to use both employees and contractors. This gives us stability and an in-house core of skilled and knowledgeable people while also enabling us to respond rapidly to client requests, even at short notice.
Focus on Teams Rather than Individuals for Project Delivery
A good analogy here is a scrum in rugby, where eight players interlink and move as one towards the same goal. Even if one drops out, the seven remaining can continue to drive forward, or a replacement can be slotted in.
Our approach to delivering projects follows a similar principle, where a tight-knit team of employees and contractors works together towards delivering on the client’s objectives. Rather than an approach where individuals perform individual tasks to make up the whole, the focus remains on the team.
Continuous Development of a Company-Wide Learning Culture
Industry experience can only deliver maximum benefits when the knowledge learned from those experiences is disseminated throughout the organisation. At SL Controls, we have well-established processes to ensure knowledge and information is available across teams and business units.
Enabling Multiple Career Path Opportunities
We embrace and nurture multiple career path opportunities based on the needs of the business instead of taking a linear approach to career progression. This ensures greater fulfilment for members of the team and helps everyone reach their full potential.
Furthermore, linking the process with the needs of the business ensures we constantly meet the needs of our clients, even as those needs evolve.
Continuous, Customised, and Multidirectional Feedback
Continuous, constructive feedback from supervisors, team leaders, peers, and managers at all levels enhances quality as well as the accuracy and speed of project delivery. It is a much more flexible and effective method of providing feedback than the traditional annual appraisal model.
Delivering for Clients
There are a number of benefits that an agile approach to talent management will bring to your business. They include:
- Availability of specialist engineers in multiple disciplines
- Those specialist engineers integrated with your team
- Vendor-neutral approach to project delivery
- Long/short term placement solutions available
- Structured management process
- In house technical support team
- Fast deployment of resourcing options
Industry 4.0 technologies and processes are transforming the manufacturing sector and will, in the near future, lead to disrupted business models. Our agile approach to talent management will help you navigate through these changes, providing you with the skills, resources, and project delivery expertise that you require.

Advantages and Benefits of Industry 4.0 Horizontal Integration for Pharmaceutical & Medical Device Manufacturers
Two concepts known as vertical integration and horizontal integration are key to moving your manufacturing facility closer to an optimised Industry 4.0 operation. We discussed the benefits of Industry 4.0 vertical integration in another blog. Here, we’ll look at the advantages and benefits of Industry 4.0 horizontal integration.
Let’s start with a recap – what is Industry 4.0 horizontal integration?
Horizontal integration is about integrating all aspects of your supply chain. This includes internal functions and processes on the factory floor, i.e. equipment systems integration across your entire manufacturing operation. This can be within a single facility or if you have a multi-site operation.
It also includes integrating with third parties in your supply chain:
- Upstream with raw material and part suppliers
- Downstream with your distribution chain all the way to the end-user, customer, or patient
As a pharmaceutical or medical device manufacturer, you may already have achieved an element of horizontal integration to meet your regulatory obligations. An example would be a serialisation or track and trace solution.
Full horizontal integration moves this strategy beyond compliance to deliver benefits for your business. It involves integrating equipment, systems, and processes to ensure real-time access to data, and to automate processes and decision-making.
The Benefits of Horizontal Integration
Streamlined Regulatory Compliance
One recent regulatory trend in both the pharmaceutical and medical device industries is the extension of compliance responsibilities across the supply chain. Track and trace, as mentioned above, is a good example, as are new requirements under the EU MDR.
Industry 4.0 horizontal integration streamlines compliance in relation to your operations and the operations of third parties in your supply chain.
End to End Visibility
Delays in production processes and workflows occur where there is a lack of information and collaboration. Industry 4.0 horizontal integration breaks down data silos to make information more accessible at each point in the supply chain. It also significantly improves collaboration.
From your perspective, you will have end-to-end visibility of your supply chain, so you know what is going on and can react to unpredicted situations quickly and effectively.
Improved Decision Making and Planning
With end-to-end visibility, you will have access to real-time intelligence that will give you more detailed and accurate information to make better decisions and improve planning.
Adaptability
With Industry 4.0 horizontal integration, your supply chain will be better equipped to deal with change and unpredictability. For example, if there is a problem with a production line, machine, or material, you will have the information you need to adjust the production workflow to minimise the impact overall.
Flexibility
You will also have flexibility with Industry 4.0 horizontal integration to react to external factors. Examples include changed regulatory requirements, as well as the impact of new technologies, competitor actions, and customer demand.
Improved Efficiency
With end-to-end visibility, all parts of your supply chain can work together more productively and effectively. The result will be the identification of efficiency savings, such as reducing inventory levels, warehouse space, or distribution costs.
Digital simulations can then drive efficiency savings beyond what was previously possible. In other words, you can run predictive algorithms and digital simulations to find new and more efficient workflows, processes, and ways of working.
Meet Customer Demand
Several of the points above culminate in making your organisation better equipped to meet customer demand. Enhanced visibility and decision making, for example, means you can react to problems that previously would have resulted in issues with product availability.
Industry 4.0 horizontal integration also makes it possible for you to react more effectively to changing market conditions as well as changing consumer, patient, and end-user expectations.
Improved Quality Control
Your quality control processes will also improve with Industry 4.0 horizontal integration as you will have enhanced visibility across the entire supply chain. This makes it easier to monitor everything from raw materials to storage processes to transportation.
Better Understanding of Customers, Patients, and End Users
Industry 4.0 horizontal integration creates a closer link between your manufacturing operation and the end-user or patient, improving your understanding. You will also learn more about how your product is used in real-world conditions.
This information can be beneficial in various areas, including business planning, marketing, and product development.
Improved Profitability
All the points above contribute to improved levels of profitability in your business. This includes ensuring your operation remains competitive as Industry 4.0 technologies continue to disrupt manufacturing sectors.
Horizontal integration also helps you maintain value when the unexpected happens or when change occurs. Examples include adapting to deal with problems in the supply chain, being flexible enough to react to changing market demands, or better planning due to enhanced supply chain visibility.
You can also reduce costs through Industry 4.0 horizontal integration as you can run a leaner supply chain. Examples here include reduced warehouse costs and avoiding the costs involved with late shipments, overages, and shortages. You will also benefit from cost savings as a result of automating processes.
Adding Value Through Horizontal Integration
Further horizontal integration is the natural direction of travel for manufacturers in most industries, particularly in highly regulated sectors. Taking a strategic approach and staying ahead of the curve will improve your competitiveness, reduce macro-level risks, and ensure you are in a position to take advantage of new opportunities.

Benefits of Industry 4.0 Vertical Integration – Where OT and IT Converge
Vertical integration is about converging OT (operational technology) and IT (information technology) in your business, in addition to integrating processes and other systems across different departments and business units.
In its most advanced form, it involves all aspects of the business, from factory floor systems and processes to the ERP (enterprise resource planning) platform, CRM (customer relationship management) system, accounting system, and more.
In many manufacturing businesses, the first step involves ensuring full equipment systems integration at the production level before then integrating with other parts of the business.
While vertical integration is typically achieved in stages, in its totality, it is a significant undertaking. It also delivers significant benefits – benefits that will ensure your business remains competitive and profitable into a future where the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, and customer/patient demands and expectations continue to change.
Improving Data Collection & Replacing Data Silos with Integrated Systems
Vertical integration in your business involves collecting more data (from sensors on production equipment, parts, and products, for example), as well as replacing your existing data silos with integrated systems. Below are the main benefits of implementing this strategy.
Production Flexibility
With vertical integration, you will be able to move towards mass customisation and lot size of one business models and production strategies. This enhanced level of production flexibility will make it possible for your business to exploit new market opportunities, react quickly to trends, and deliver on the expectations of customers/patients.
Production Adaptability
Vertical integration will improve the resilience of your manufacturing operation. In other words, making it possible for you to adapt to changing circumstances (such as unplanned downtime) more quickly while also minimising the impact of changed circumstances on customers/patients.
Increased Market Agility
Both the above points give senior executives the options they need to react more effectively to market and business conditions. This could be anything from reducing risk to remaining competitive to taking advantage of a new opportunity.
Improved Security and Privacy
One of the technologies that make Industry 4.0 vertical integration possible is cloud computing. With cloud computing, systems run on the cloud and data is stored in the cloud rather than on-site at your facility.
These cloud solutions are typically built on enterprise-standard platforms like Microsoft Azure. As you might expect, enterprise-standard platforms like Azure come with enterprise levels security.
Therefore, you will enhance security and privacy in your business by implementing cloud technologies (alongside also implementing relevant security processes and procedures) as part of a vertical integration strategy.
Improved Management Oversight and Visibility
Vertical integration provides engineers, managers, and executives with access to greater levels of accurate, well-presented, and highly relevant data. Not only that, but the data is available in real-time.
Enhanced Levels of Automation
Vertical integration increases the processes in your operations that you will be able to automate. Machine maintenance, production planning, and raw material ordering are just some examples.
Enhanced Productivity
Productivity levels in your business will improve in a number of areas, not least because all departments and systems will work together more effectively towards the same goal. Even ensuring each person on your team has ready access to information improves productivity as time is saved compared to the previous process of requesting information and then waiting on a response.
More Efficient Operation
You will benefit from efficiency savings too, through productivity gains and enhanced automation, as well as by reducing unplanned downtime, improving access to information, faster decision-making, and more.
Enhanced Customer Service
Responding faster to market conditions, trends, and consumer demands improves standards of customer service.
The integration of customer-facing departments with the production line will also improve customer service. An example of this is customer-facing staff being able to provide information, assurances, and updates to customers based on real-time production information.
Reduced Requirement for Physical Equipment
Converging OT and IT in your business, as well as implementing cloud technologies, should result in a reduced need for physical equipment on-site. This delivers a range of additional benefits including:
- Lower costs for IT and OT infrastructure
- Reduced requirement for physical space for IT and OT infrastructure
- Reduced energy consumption which also lowers costs while helping you achieve your environmental and CSR goals
- Improved performance, particularly in relation to systems and processes moved to the cloud
- Reduced maintenance requirement
Improved Profitability
The above benefits combined will deliver higher levels of profitability for your business in addition to ensuring you achieve your ROI objectives.
Moving Your Business Forward
It is likely that you will already have achieved a level of vertical integration in your business, particularly if you have implemented automation and/or equipment systems integration solutions.
Going further using a staged approach is the way forward with vertical integration, where you measure improvements and realise the benefits at each step.
Horizontal and Vertical Integration in Industry 4.0 for Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Manufacturers
In an Industry 4.0 context, horizontal and vertical integration offers substantial benefits to pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers. These benefits include everything from improved agility and flexibility to enhanced productivity, decision-making, and competitiveness.
Horizontal and vertical integration delivers these benefits by achieving unprecedented levels of alignment across entire organisational ecosystems, from the factory floor to enterprise-level systems, across the supply chain, and in all processes, business units, and third-party partners.
Defining Industry 4.0 Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration and vertical integration are terms used in various contexts, including in relation to business growth strategies. Specifically, it refers to acquisition strategies where companies use horizontal integration to acquire companies with similar products and customers or vertical integration to add new capabilities and bring outsourced services in-house.
However, within the field of Industry 4.0 and the pursuit of the Smart Factory goal, horizontal and vertical integration have a different meaning.
The two concepts centre on technologies, processes, and systems that enable the collection, collation, communication, and use of data.
Industry 4.0 Vertical Integration Explained
Industry 4.0 vertical integration involves connecting all business units and processes within your organisation. In other words, converging operational technology (OT) at the production level with information technology (IT) at the enterprise level.
With this integration in place, data flows between and is made available to all business units. This includes the factory floor, marketing, sales, customer service, purchasing, accounting, HR, quality control, R&D, and more.
Vertical integration isn’t just about integrating enterprise-level systems with the factory floor, however, as it also creates opportunities for integration across the entire field layer of your organisation.
A good example of this is in the batch-size-of-one business model where a customer requests a product customisation. Instead of the sales department retrieving information from production on whether the request can be delivered, the information will be readily available in the ERP system.
Another example is the alignment of raw material procurement with market demand to maximise the efficiency of batch production.
Industry 4.0 Horizontal Integration Explained
While vertical integration involves alignment within your organisation, Industry 4.0 horizontal integration involves connecting all parts of your supply chain. This deeper alignment improves visibility, flexibility, and productivity while also enhancing levels of automation.
Horizontal integration applies within your production facility, across multi-site operations, and to third-party partners in your supply chain, both upstream and downstream.
Within your production facility, horizontal integration is about achieving the Smart Factory, where all systems, processes, and machines are connected, enabling constant communication.
Horizontal integration delivers the same level of connectivity across multi-site operations, ensuring maximum visibility, production adaptability, and collaboration.
The real-game changer is achieving similar levels of decentralisation and connectivity across your entire supply chain, from suppliers and manufacturing through to logistics and distribution, all the way to the customer/patient.
Industry 4.0 technologies make the above integration goal possible in all manufacturing industries, but there are additional considerations in regulated sectors like pharmaceuticals and medical devices. This particularly applies to traceability requirements where serialisation and track & trace solutions are essential components.
Continuing the Journey
Following on from the point above, by implementing a serialisation or track & trace solution, something which is necessary for regulatory compliance, you have already started on the road to Industry 4.0 horizontal integration.
You may also have achieved a level of Industry 4.0 vertical integration.
As with all aspects of Industry 4.0 and the implementation of new technologies, processes, and systems in your business, it is a journey. There is a direction of travel, though, particularly for manufacturers in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. That direction of travel is towards the achievement of Industry 4.0 horizontal and vertical integration.

The Human-Centred Approach: A Key Component to Industry 4.0 Success
Industry 4.0 is transformative. Among other things, it enables you to move from being a product-centric organisation to being customer-centric. This presents massive and potentially game-changing opportunities for your business.
Implementing Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory solutions is, of course, a marathon rather than a sprint. That said, even in the early stages of the transformation, all areas of your business are likely to see an impact. This includes manufacturing, product design, supply chain management, customer service, corporate strategy development, and more.
This covers a lot of people on your team. In fact, your whole team is likely to be impacted at some point by Industry 4.0 transformation.
Industry 4.0 is About More Than Technology
A lot of the discussions that take place in relation to Industry 4.0 focus almost entirely on technologies. In other words, how the development of new technologies has ushered in the era of Industry 4.0, making it possible to develop Smart Factories and truly digitalised organisations.
Processes often come up in these discussions too, whether that is equipment maintenance processes, validation processes, regulatory compliance processes, quality management processes, etc.
However, the people element of implementing Industry 4.0 initiatives and solutions is too often forgotten about completely. When the human factor is mentioned, it is usually relegated to points regarding efficiency savings, i.e. the potential for headcount reductions or resource redeployments.
From our experience at SL Controls implementing Industry 4.0 solutions for pharmaceutical and medical device industry clients, people are core to achieving success.
We believe people are as important, if not more important, than the technologies that we are all rightly excited about using, developing, and creating.
Not only are people directly impacted by the operational and business transformations that Industry 4.0 makes possible, but they are crucial to every stage of solution and technology implementation.
People-Centric Leadership
Managing change, implementing new technologies and processes, and making the most of the opportunities that Industry 4.0 presents, requires a people-centric leadership approach.
This means ensuring your team, particularly those at the coalface, have the knowledge and skills they need. You also need to engage them in both the overall strategy of the business and in individual projects, and they need to be empowered.
The worst case is when those on the frontlines feel disconnected, afraid, and frustrated with the changes you are implementing.
Instead, they should feel part of the Industry 4.0 development process, fully engaged with the principle of continuous improvement and the pursuit of excellence.
Human-Centred Design
The approach of Industry 4.0 solution providers is important too. The best results are achieved collaboratively through human-centred design.
In other words, the traditional ways of developing and implementing technology solutions are not effective in the Industry 4.0 world. These conventional approaches are top-down, where executives and managers decide on a solution that they believe will benefit the company before overseeing the development and implementation in partnership with a solution provider.
From a technical point of view, the technology works, so the executives and managers move to the phase of overseeing frontline worker training before telling those frontline workers to get on with it.
Unsurprisingly, the new solution rarely sticks the way the leadership originally planned, and the results rarely live up to expectations.
Instead of focusing on developing technology and then figuring out how to make it stick, the better approach is to focus first on the perspectives of users: how they work, their pain points, the challenges they face, how and why they use information, where their data comes from, how they think things could be done better.
You need strong executive and management level support too, of course.
Support from the other side – bottom-up support – is also essential. This means not only getting buy-in but proactive engagement from operators, technicians, and engineers on the factory floor as well as team members in other business units and departments.
Focusing on Business Objectives
Recent history is littered with stories of technologically fantastic solutions that are only used to a fraction of their capabilities because of a failure to take a human-centred approach in their design and implementation.
Industry 4.0 technologies offer opportunities to members of your team at all levels to develop their skills and become an integral part of this ongoing industrial revolution. We need to facilitate and nurture the potential of all people in our industries. This will help achieve Industry 4.0 success as well as your medium and long-term business objectives.
« Previous 1 … 6 7 8 9 10 … 18 Next »




