Blog
The Relevance of OEE in the Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory Era
OEE is a well-established method of measuring productivity in manufacturing operations. Its origins can be traced back to the 1950s, however, so does it still have relevance today in the Industry 4.0 era?
Not only is OEE still relevant, but its importance has been amplified with the opportunities and challenges created by Industry 4.0 technologies and processes, as well as the ongoing push to develop the Smart Factory of tomorrow.
In-Brief OEE Definition Recap
OEE is a calculation that measures machine availability, performance, and quality. So, a score of 100 percent means you are manufacturing with no downtime and as fast as possible while only producing good products with zero defects.
Getting as close as possible to this 100 percent ideal means you are maximising your facility’s productivity.
The Modern Realities of Manufacturing Facilities
Today, there is an ever-increasing requirement on manufacturing facilities to produce high-quality products while meeting often challenging production timescales.
These requirements are being driven by things like increasing consumer expectations, greater industry competitiveness, and, in relation to sectors like pharmaceuticals and medical devices, the demands of regulators.
With Industry 4.0 technologies, we are also moving closer to mass customisation and batch size of one production capabilities, increasing the need to monitor, improve, and maintain productivity even further.
How OEE Fits into These New Manufacturing Realities
While OEE has been a productivity performance metric for decades, it has never been more important than it is now.
Even with new technologies, systems, platforms, and processes, it remains the best way of benchmarking the productivity of your operation. It can help you identify areas for improvement before giving you a tool to objectively monitor your progress towards an enhanced level of productivity.
OEE in the Industry 4.0 Era
So, OEE as a productivity performance metric is more important today than ever before. We can take this a stage further, though.
This is because Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory technologies enhance OEE effectiveness as a manufacturing productivity measurement. It does this by improving the accuracy of OEE calculations. There are several reasons for this:
- Enhanced levels of equipment integration – equipment systems integration is often the starting point for implementing Industry 4.0 solutions into your production facility. In relation to OEE, integrated systems and equipment improve the value of the data you collect for OEE calculations.
- More data points collected – sensor technologies are another crucial component of solutions that fall under the Industry 4.0 umbrella. These sensor technologies make it possible to collect multiple data points within a machine, section, production line, and overall facility.
- Higher data sampling rates – sensors, networking infrastructures, and cloud computing means you can collect data with sampling rates as high as you need them.
- Improved data quality – sensor technologies and modern data collection and processing systems improve the quality and accuracy of data used in OEE calculations.
- Improved contextualisation and processing of data – this is delivered through big data solutions, machine learning, data dashboards, and more. For example, data can be used by a machine-learning algorithm to move to a predictive maintenance model for machines rather than a scheduled maintenance model, with the driver for this change being an improved OEE calculation.
Proactive OEE Improvements
Industry 4.0-related technologies and solutions also make it possible to improve OEE proactively rather than always being reactionary. This takes OEE calculations beyond real-time monitoring of data into predictive modelling of different scenarios.
The specific technologies that make this possible include digital twin and virtual simulation technologies. With these technologies, you can model different scenarios to analyse their impact on OEE without interrupting the live production line. The results of these models can then be used to make changes that will improve OEE.
Staying Focused on Return on Investment
With all the above, the most important factor is return on investment, whether that is through enhanced profitability by improving productivity, greater competitiveness in the market, or the capability to explore new business and product development opportunities.
This, whenever everything else is said and done, is what OEE is about, i.e. giving you an objective tool to measure return on investment from your Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory initiatives.

Industry 4.0 and the Importance of Technology, Executive Support, and Skills Alignment
Often when discussions take place around Industry 4.0, they revolve around technologies. In other words, how technologies like cloud computing, robotics, AI, digital simulations, autonomous vehicles, data analytics, etc are creating opportunities for manufacturers to move into the Industry 4.0 era.
Industry 4.0 is about much more than technologies, however. Instead, it is about digitally transforming your business and developing deeper integrations and more efficient workflows between all components in your organisation. This includes manufacturing, supply chain, product development, marketing, sales, customer support, HR, and finance.
Therefore, to maximise the benefits of Industry 4.0 and remain competitive in the digitally transformed world of tomorrow, you need to develop an alignment of technology, executive support, and workforce skills.
Transforming Your Entire Business
Industry 4.0 is a journey, but the endpoint is likely to be a very transformed business model. Examples of how this might look include batch size of one manufacturing capabilities or mass customisation.
This demonstrates that Industry 4.0 doesn’t just impact the factory floor and closely connected business functions, such as the supply chain. Instead, opportunities and transformation potential exist across the entire business.
Executive Support
As a result of the above, Industry 4.0 requires executive-level buy-in at an early stage.
This doesn’t just mean buy-in for the next project you plan to complete as part of your Industry 4.0 journey, but buy-in for the overall concept and potential of Industry 4.0.
Here is an example of why this is important: Industry 4.0 processes, technologies, and solutions that can be implemented today can give you substantially greater insight into your customers and a better understanding of emerging market trends. This is achieved by integrating the marketing and sales functions of the business with the manufacturing and product development functions.
Solutions like this give senior executives access to data that enables them to pivot and adapt the company as required to meet customer demand and expectations.
However, the technology that makes it possible for executives to access and analyse this information is only an enabler. Executives still need to make decisions in the best interests of the company.
This requires a collaborative approach across all parts of the organisation as well as fast decision-making processes to ensure opportunities can be seized upon quickly.
For this to happen, you need executive-level buy-in.
Furthermore, with executive-level buy-in, it will be much easier to get buy-in across the wider organisation. This is another important element of successful Industry 4.0 implementation, particularly as the solutions you implement become more advanced.
Upskilling Your Team
The fact that technology is an enabler of Industry 4.0 applies right through your workforce in addition to at the executive level.
Also, almost all Industry 4.0 technology solutions have a human element. This includes operators and engineers as well as data analysts, product designers, and other roles across the company, i.e. not just in production.
Therefore, upskilling your team is a crucial part of Industry 4.0 success.
With the introduction of Industry 4.0 solutions, advanced capabilities will be available to your organisation in a range of areas. Your team needs the necessary skills to ensure you can capitalise on them.
People and Processes
The benefits of Industry 4.0, and the opportunities it offers your business, are substantial. In fact, there are likely to be opportunities and benefits that we can’t yet quantify or fully understand.
However, looking at Industry 4.0 as a technology issue, or even a manufacturing issue, will limit your potential.
The reality is that Industry 4.0 is about people and processes as much as it is about technology. Having all the right elements aligned will ensure you maximise success.

Digital Validation and Why It’s Important to Pharmaceutical and MedTech Manufacturers
Modern technologies make it possible to create digital simulations, digital twins, and virtual 3D models of products, parts, manufacturing processes, machine processes, systems, and more.
Engineers can then use these simulations and models to facilitate the design process, improve quality, identify errors, and improve performance. They can do this by testing multiple design variations in multiple environments under multiple conditions.
For many industries, including pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing, this is a game-changer.
However, what happens if the digital simulation is incorrect or inaccurate? Of course, the answer is the results produced by the simulation or model will also be incorrect or inaccurate.
Enter digital validation.
Digital validation is a process that, in simple terms, ensures the accuracy and correctness of digital simulations and models.
This gives everyone, from engineers to decision-makers to end-users, confidence. Confidence not only in the simulation or model but also in the real-world outputs that result, i.e. outputs such as product design changes, changes to processes, etc.
The Importance of Digital Models and Simulations
The digital modelling tools that are currently available make it possible to create powerful thermal, mechanical stress, injection moulding, computational fluid dynamics, and circuit simulations in a virtual environment.
This can help determine things like the best materials to use in a product, for example, or the design and shape of various parts. It’s also possible to use simulations to identify failures that occur over time, i.e. failures that are hard to identify with a physical prototype.
Furthermore, digital models of products, parts, processes, or systems can be simulated in various environments and under a range of different conditions.
This provides engineers with accurate data to make decisions so eliminates common issues that can cause problems, such as making educated guesses or over-engineering products.
Benefits of Digital Models and Simulations
The potential benefits of digital models and simulations to manufacturers in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries are substantial. They include:
- Reduced time to market for new products because design changes can be implemented and tested in a virtual environment speeding up the iterative process
- Reduced costs at all stages of a product’s lifecycle but particularly in the product design stage as digital simulations and models are highly effective at avoiding downstream design changes
- Improved quality of existing products
- Improved OEE and manufacturing productivity
- Helps ensure regulatory compliance and streamlines compliance processes, particularly when getting approval for a new medical device
The Need for Digital Validation
Creating a digital simulation of a product or part is not enough, however, particularly in highly regulated industries like pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturing. This is because each stakeholder in the process, from company decision-makers to regulators to end-users and patients, needs to know the simulation, and the results it produces, are correct.
Also, while the technology that exists today is extremely powerful and can now produce virtual models that are very close to being exact replications of real-world products, parts, and processes, close to exact is not the same as exact.
The existing paper-based process for validation of existing products, parts, manufacturing processes, machine processes, and systems is extremely time-consuming, labour intensive, and inefficient, and will potentially negate the benefits of digital models and simulations.
As a result, a new approach for the validation of digital models for their intended purpose is essential.
How Digital Validation Works
Digital validation is an iterative process that happens during the development of the simulation. Since the digital simulation of a product or part is available during the design stage of the project, digital validation can begin at this stage. Test simulation models can be built to test the user requirements and verify that these requirements are being met. These test simulation models are automatically updated with any changes to the model and can be re-executed at any time to verify that the model still meets the original user requirements. The digital validation process ensures, confirms, and quantifies the accuracy of the simulated model.
This could be accuracy compared to the real-world product, part, process, or system. It could also be accuracy compared to the conceptual description of the model or accuracy compared to experimental data.
The digital validation process significantly reduces the level of effort involved to qualify products, parts, manufacturing processes, machine processes, and systems, which, in turn, significantly reduces the associated validation costs.
Typically, the validation process ensures the simulated model is accurate within an acceptable range for the intended purpose of the model. Therefore, it’s important to create simulated models for a specific purpose.
Maximising Benefits
So, in summary, digital models and simulations provide significant opportunities for pharmaceutical and medical device companies while digital validation ensures the validity of those simulations, giving them measurable and fully documented credibility while also making validation more efficient and affordable.

How Developing a Digital Supply Chain Will Improve Your Business
In a previous blog, we outlined what the digital supply chain looks like in the Industry 4.0 era. To briefly recap, it is not just about operating digitally – communicating digitally, analysing data digitally, etc.
Instead, it is about connecting all elements in your supply chain in real-time, providing you with simultaneous and instant communication capabilities as well as real-time oversight of your supply chain’s component parts.
Why is this important? How will implementing digital supply chain technologies and processes improve your business?
What is Wrong with Current Supply Chain Management Processes?
Let’s first look at the problems that exist with current supply chain management processes. Those problems include:
- Poor visibility and oversight – you are likely to have limited access to data from the elements in your supply chain, and that data will not be in real-time. This lag in data access forces reactionary decision-making rather than predictive decision-making.
- Slow decision making – following on from the above point, the entire decision-making process operates slower than it should.
- Lack of operational certainty – slow, reactionary decision-making creates operational uncertainty. Another contributing factor to this uncertainty is the lack of real-time oversight of elements in your supply chain.
- Unaligned objectives – the different elements in your supply chain will face different pressures and will have different priorities. For example, one stakeholder might underestimate capacity as it doesn’t want to fully commit what is available because bottlenecks in other parts of the supply chain in that past left its capacity unused.
- Lack of trust between stakeholders – the above creates a lack of trust between stakeholders in the supply chain, where the various elements have competing priorities, i.e. their own interests and the interests of the supply chain/manufacturing operation.
How the Digital Supply Chain Will Transform Supply Chain Management
For companies like us at SL Controls that work daily with Industry 4.0 technologies, we talk a lot about business transformation. Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies is, of course, an evolutionary process, but the solutions and systems that we implement are transformational.
This applies to the digital supply chain too. Below are some of the main ways the digital supply chain transforms manufacturing businesses.
- With fewer manual processes in the supply chain, accuracy and speed improve. This improves the service you provide to customers. For example, the digital supply chain is an important component to achieving batch-size-of-one operational capabilities.
- Predictive analytics, predictive maintenance, big data, and machine learning increases OEE and production uptime.
- The digital supply chain also enables predictive decision-making. Most manufacturing facilities currently look backward when analysing supply chain data. Companies with more advanced systems and processes have moved to a point where they have access to some real-time data. This is limited, however. Accurately predicting future outcomes and situations in the supply chain based on real-time data is the real game-changer, though. By moving to a digital supply chain and implementing other Industry 4.0 technologies, predictive data analysis is possible.
- With the digital supply chain, you can move away from repetitive tasks that generally do nothing more than keeping things ticking over in your supply chain. Instead, you can allocate resources to planning, strategy development, and performance improvement.
- The digital supply chain enables a more collaborative approach between different functions in your organisation as well as different elements in the supply chain. For example, the digital supply chain can align objectives and priorities while also increasing visibility and trust.
Moving Forward
The manufacturing operations that will remain competitive in the future will be those that move beyond the hybrid supply chain situation we have now, where there are digital components, but processes are manual and reactionary. The digital supply chain is the future.

The Importance of Industry 4.0’s Digital Supply Chain
Traditionally, supply chain management was a back-office function in manufacturing businesses. It was important, of course, particularly in regulated sectors like pharmaceuticals and MedTech, but it wasn’t central to the performance and management of the company. In other words, it wasn’t on the day-to-day radar of C-Suite executives – CEOs, CFOs, etc.
This is changing as companies embrace Industry 4.0 technologies and move towards digital supply chain solutions. They are doing this to remain competitive and meet customer expectations as existing systems are rapidly becoming unfit for purpose.
A new reality is now developing, a reality where supply chain management influences all aspects of the business from strategic planning to corporate reputation to sales to product development and more.
The Evolution of the Supply Chain
In the past, supply chain management was a manual process. Records were kept on paper (if they were even kept) and communications, data analysis, decision-making, approvals, etc would all have been physical processes.
Today, many elements of supply chain management are now digitised. In fact, in some businesses, there is extensive digitisation.
So, there is more data, with much or all of it stored digitally. This makes it easier and faster to access than physical records while also improving accuracy.
Communications are also digital, with technologies like email, video conferencing, screen sharing, etc.
Software is used to enhance decision making by, for example, providing managers with dashboards to help them better understand the data that has been collected. This improves oversight of both the manufacturing and supply chain management processes.
However, even though a lot of elements in the supply chain are digital, this is not the digital supply chain.
The Hybrid Supply Chain
What we have now in most manufacturing operations is best described as a hybrid supply chain. Various elements have been digitised, but processes are still manual, albeit with the use of digital technologies.
Look at an example of a customer who wants to significantly increase the number of products it intends to purchase. Confirming there is capacity in your supply chain to meet this increased manufacturing demand could take days or weeks. This is because the process of communicating with, and getting agreement from, the various components are still manual, i.e. emailing, phoning, or video calling a supplier in your supply chain is a manual process.
After several days, you get assurances from the various points in your supply chain that they can meet the increased demand, so you ramp up your manufacturing operations to deliver the client’s bigger order.
However, you have limited oversight of how those in your supply chain are delivering on their promises. As has always been the case, a supply chain is only as strong as its weakest point. You have minimal oversight over those weak points… of any points in the supply chain, in fact.
This is because the supply chain data you have is limited and is not real-time, resulting in situations where the first time you hear there is a bottleneck or quality issue, for example, is when the problem is already live and has already impacted output.
The Digital Supply Chain
Here is where the digital supply chain really shows how it can benefit manufacturing businesses. In the digital supply chain, every point is connected, making data available in real-time via the cloud.
In the above example, informing and getting commitments from the various components in your supply chain for the increased order would be simultaneous, with that measured in minutes and hours rather than days or weeks.
In addition, you would have real-time oversight over each element of the supply chain, giving you real-time information on everything from quality control to production rate.
Combine this with big data and dashboard technology, and you move from being a reactionary manufacturing operation to operating on a reactive and preventative basis.
This enables you to deliver on the objectives mentioned at the start of this blog – meeting changing customer expectations and remaining competitive – as well as other objectives important to your business.
As a result, the digital supply chain should not be considered a future concept but should be a high priority for your organisation today.

Infographic – Lean Validation
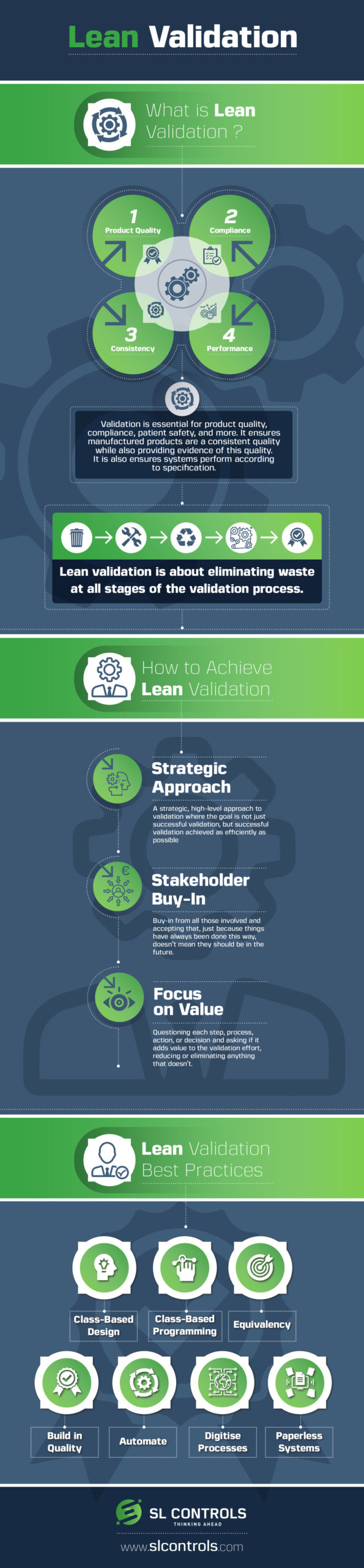
What is Lean Validation?
Validation is essential for product quality, compliance, patient safety, and more. It ensures manufactured products are a consistent quality while also providing evidence of this quality. It is also ensures systems perform according to specification.
Lean validation is about eliminating waste at all stages of the validation process.
How to Achieve Lean Validation
Strategic Approach
A strategic, high-level approach to validation where the goal is not just successful validation, but successful validation achieved as efficiently as possible
Stakeholder Buy-In
Buy-in from all those involved and accepting that, just because things have always been done this way, doesn’t mean they should be in the future.
Focus on Value
Questioning each step, process, action, or decision and asking if it adds value to the validation effort, reducing or eliminating anything that doesn’t.
Lean Validation Best Practices
- Class-Based Design
- Class-Based Programming
- Equivalency
- Build in Quality
- Automate
- Digitise Processes
- Paperless Systems
Read more about lean validation.

The Importance of Transforming Remote Support and Collaborative Working Across Companies
The technologies that exist today make remote collaborative working across companies easy. The same applies to providing remote support services for IT systems.
You can jump on a videoconference call using any number of applications. At the end of the call, you can give control of your computer to the third-party engineer you’ve been collaborating with, so they can access your company’s IT system to complete the necessary changes.
You can even watch the engineer do this, all in real-time, but you probably won’t as you have other tasks to complete and meetings to attend.
There’s more. If you need to share a document, no problem. Just open the chat facility and click send. Bring another engineer, vendor, or colleague in on the call? Yep, you can do that too.
Not only can you do all the above, but you can do it regardless of location. The engineers and vendors collaborating with you can be on the other side of the world or they can be in the building next door. It makes no difference to the capabilities of the technology.
You can even take it a stage further using Microsoft’s HoloLens mixed reality technology to allow those collaborating on the project or task to see and work with physical objects even though they are not in the same location.
All the above is relatively straightforward, but there is one major flaw – security.
The Security Challenge of Remote Collaborative Working and Support Provision
Let’s look at the above scenario again.
- You jump on a videoconferencing call using a non-enterprise application, opening your organisation to multiple security risks.
- You let an engineer from another company take control of your computer to make necessary updates or changes to your IT system, but how do you know what they are really doing? Even if you sit and watch, you may not know everything that is being done.
- In the hours, days, weeks, or months after the engineer finishes, you might need to see and understand what was done to, for example, correct an error that has occurred. You have no record of the work, however, so have no straightforward or quick way of checking.
- You send an internal company document through a chat facility, but that document is now on the IT system of one or more third-party companies. It could then be accidentally or deliberately shared with one of your competitors.
You get the idea.
The Security Reality
Remote collaborative working and support provision are easy with technologies that currently exist.
This doesn’t mean those technologies are suitable for corporate environments, however. In fact, with many of the technologies out there, particularly those where there are known and suspected security flaws, they are not only unsuitable but also dangerous.
Applications such as Google Hangouts, Facetime, WhatsApp, Instagram, Zoom, etc are convenient and even beneficial for personal use. However, the incorrect use of these platforms creates significant risks, raising questions over their suitability for use in corporate environments.
You then need to throw into the mix the growth of the gig economy, where self-appointed experts provide services on a task by task basis.
Technology makes it possible to collaborate with freelancers, but is this really the best approach? How do you manage Non-Disclosure Agreements? How do you ensure the freelancer has the necessary competencies, systems, and policies to meet your compliance requirements?
As with the technology question, just because working with freelancers is possible, doesn’t mean you should.
That said, you don’t need to abandon the idea of remote collaborative working and support with third-party companies and others. Instead, you need to adopt a similar approach to the design and commissioning of your internal VPN.
This means developing proper procedures and policies.
It also means using technology that has enterprise-focused security at the core.
The Microsoft Teams Solution
Microsoft Teams is central to the above solution. It has all the functionality required to work collaboratively and remotely across different organisations.
It also has all the security and control functionality required to ensure your organisation’s IT infrastructure, intellectual property, and confidential data remain secure.
Let’s go back to the example above:
- You connect with third-party engineers and vendors in a Microsoft Teams videoconferencing call that you set-up. This gives you control over all aspects of the call in a safe environment protected by Microsoft’s enterprise-level security.
- You can let an engineer from another company take control of your computer using Microsoft Teams AND you record everything they do so you have video evidence and backup if it’s ever required in the future.
- Instead of sending an internal company document, you share it within Microsoft Teams, ensuring you retain full control of access and distribution.
Protecting Your Organisation in the Remote Working Era
Remote working, remote collaboration, and remote support will become more common in the months and years to come. After all, remote working offers huge productivity, efficiency, and cost-saving benefits.
The technology that is currently available has made remote working too easy, however, exposing companies in all sectors to significant security risks.
Transforming your approach and using the right technologies mitigates these risks, allowing you to take advantage of the benefits of remote working while keeping your company’s systems, assets, and data secure.

The Impact of Industry 4.0 on New Business Opportunities in Pharma and MedTech
Industry 4.0 technologies allow your business to improve efficiency, enhance the service you offer to customers, and increase profitability in your current manufacturing operations. These are compelling reasons for developing and implementing an Industry 4.0 strategy.
Industry 4.0 is about more than enhancing and improving your business operations, though. The technologies, processes, and ways of thinking that are part of Industry 4.0 also create new business opportunities.
Plus, here’s the thing: whether your manufacturing facility and wider organisation take advantage of these new opportunities or not, others will.
These business opportunities were highlighted in Ireland’s Industry 4.0 Strategy 2020-2025, published in December 2019 by the Department of Business and Innovation. Let’s look at them in more detail.
Producing Targeted Products
We are moving towards a situation where patients and consumers will take medicines and use medical devices that have been personalised for them at the manufacturer. This will be possible across the entire patient experience, from diagnostics to prescribing to treatments.
The level of customisation that will be possible with batch-of-one manufacturing capabilities will be substantially more than is the norm at the moment.
Furthermore, this shift to targeted healthcare products will take on a snowball effect that will get bigger and faster as it gains momentum.
Information-Based Medicine
This involves the use of data to improve treatment and diagnostic decisions by medical practitioners, predict outcomes on an individual and group basis, and generally improve the quality of healthcare that everyone receives.
Technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, sensors, data analysis, and wearable technology make this possible. Manufacturing approaches like mass customisation and flexible batch manufacturing are important too.
In other words, establishing a greater connection between the factory floor, medical practitioners, and patients with the objective of improving health outcomes.
Connected Health and Medicine Delivery
Following on from the above point, the development of end-to-end medical devices, connected health, medicine, and drug delivery solutions is going to be transformative for patient care and health outcomes.
Patient-Focused Mindset
You can see from the above Industry 4.0 business opportunities that they are all centred on improving the quality of care delivered to patients. Often, however, conversations regarding Industry 4.0 mainly focus on business improvements:
- Improved OEE
- Productivity gains
- Reduced equipment downtime
- Expanded automation
- Improved management oversight
- Efficiency improvements
- Enhanced profitability
All of these things are important.
However, the most significant beneficiaries that will emerge in the pharmaceuticals and medical device industries in the years to come, those who will be referred to as disruptors, will be those who take a patient/consumer-centric approach.
Business and Industry Transformation
The technologies that are available and that are being developed will change healthcare and patient outcomes forever. This is where the most significant benefits of Industry 4.0 can be found.
There will still be challenges, of course. After all, while there are only a couple of letters that differ between the words “digitisation” and “digitalisation”, the impact of these two concepts on operations and business models is barely comparable.
While most manufacturing operations in the pharmaceutical industry and medical device industry around the world are moving towards an advanced “digitisation” stage, “digitalisation”, business transformation, and the major benefits of Industry 4.0 should be on your radar too. There is too much potential in the new business opportunities not to.

Industry 4.0 and the Manufacturing Industry in a Post COVID-19 World
Manufacturing operations globally are seeing disruption they have never experienced before as a result of the COVID-19 emergency. The focus in the early weeks of the crisis was about understanding and adapting to the dramatically changed situation while those manufacturing essential products like food, medicines, PPE, and medical devices dealt with the challenge of meeting demand.
Thoughts are now turning to the future for manufacturers in all industries as plans are being drafted for the slow march towards normality, albeit a normality that is likely to be different to the normal we were familiar with before.
What role will Industry 4.0 have in the post-COVID-19 world? Has the experience of the medical crisis and the resulting lockdown changed priorities in relation to Smart Factory technologies, digital transformation, and digitalisation? What are the solutions that will be important elements of the new paradigm for the manufacturing industry?
The Impact of COVID-19 on the Manufacturing Industry
How has the COVID-19 crisis impacted the manufacturing industry? Of course, there is no single answer to that question as the position varies from industry to industry and company to company.
Some have stopped production completely while others have seen massive increases in demand. There are others too who are still operating but at a reduced level while there are some that are operating but are producing completely different products than they were before the COVID-19 crisis began.
The only thing we can say with certainty, however, is that almost every manufacturing operation in every industry has been impacted by the COVID-19 crisis in some way.
This applies even in industries like pharmaceuticals and medical devices. While manufacturers in these industries mostly (although not always) fall into the category of businesses that have seen increased demand during the COVID-19 crises, they still face significant disruption.
In the pharmaceutical industry, for example, supply chains faced disruption as many of the active ingredients in pharmaceutical products come from China, the country first hit by COVID-19 and where the first lockdown and quarantine rules came into force.
Evaluating and Analysing the Impact
In the lockdown phase of the crisis, particularly in the early stages, our own health, as well as the health and wellbeing of our family, friends, and colleagues, were the most important considerations.
This continues, plus there is also a focus on ensuring the health system doesn’t become overwhelmed while we all do what we can, individually and as a wider society, to slow the spread of the virus.
As the situation unfolds, however, the economic, business, and job security impact of the crisis is coming into increasing focus as businesses plan for the next stage, i.e. when lockdown measures begin to be lifted in the coming months.
Whatever the impact of the crisis on manufacturing businesses, the situation presents a unique opportunity to evaluate and learn lessons:
- What weaknesses can be identified?
- Has the risk matrix changed?
- Was the decision-making process efficient during the most frantic stages of the crisis and was there enough information to make good decisions?
- Was the information accurate?
- Etc
Even in manufacturing businesses that have seen consistent or even increasing demand, there are still important lessons to be learned, including those above.
Learning these lessons is crucial for business resilience and continuity planning, but for the pharmaceutical and medical device industries, it is also about public health, patient outcomes, and saving lives.
Important Lessons Learned
What are some of the lessons we have learned in the manufacturing industry during the COVID-19 crisis? Accepting the fact there are challenges and limitations when making generalisations, there is an important lesson that most manufacturers can learn.
That lesson is that once system architectures and processes were tested beyond what we used to regard as a normal operating range, they failed.
There will be exceptions and there will be success stories, but most companies struggled with a new reality that they had never planned for or anticipated. For example:
- How do you maintain capacity and quality standards while ensuring sufficient social distancing for members of staff?
- How do you respond quickly to the rapidly changing levels in demand that were experienced by many manufacturers, particularly given the lack of real-time data providing information on things like raw material stock levels, manufacturing capacity, and distribution chain efficiency?
- How can you mitigate supply chain and distribution chain unpredictability?
This brings us to another lesson learned as a result of the COVID-19 crisis – the fact that manufacturing really is a real-time process. Delays, however small and wherever they occur, can have a significant impact, i.e. assessing levels of demand, raw material availability, staffing availability, scalability, the effectiveness of the distribution chain, factory floor processes, etc.
The Role Industry 4.0 Can Play in the Post COVID-19 World
Industry 4.0 was important before the crisis, not least because of the efficiency, competitiveness, and productivity benefits it offered. In summary, the technologies and concepts that fall under the Industry 4.0 umbrella set out a blueprint for the Smart Factory of the future.
This will undoubtedly change given our individual and collective experience of Q1 and Q2 2020.
Industry 4.0 technologies and solutions, however, remain important and will play a key role in shaping the manufacturing sector in the months and years to come.
Here are some of the ways Industry 4.0 solutions will improve manufacturing operations and businesses post COVID-19:
- Providing real-time visibility of manufacturing operations across all aspects of the business, breaking down data silos and ensuring real-time information is available to decision-makers
- Improving OEE, an objective which is more important now than ever before
- Increasing use of automation, robots, cobots, and autonomous vehicles for efficiency and cost-saving purposes as well as to facilitate social distancing
- Increasing use of machine learning and artificial intelligence to assess, plan, and make decisions on everything from manufacturing output capacity to equipment maintenance schedules
- 3D printing of components and parts as a backup to, or in place of, third-party suppliers
- Augmented and virtual reality for training, technical support, and other tasks which are otherwise difficult in an era of social distancing
Adapting to the New Normal
Like all sectors, the manufacturing sector will go through a period of change in the post-COVID-19 world. Industry 4.0 technologies and solutions will help manufacturing companies protect their staff and ensure output capacity while also helping them adapt to what will become the new normal.
« Previous 1 … 7 8 9 10 11 … 18 Next »




