The unified namespace (UNS) is a hot topic in manufacturing right now, largely because it is a key component to digital transformation success. We’ll explain what UNS is in this blog and why it is so important. At a high level, it is about data, integration, and communication.
Data, Integration, and Communication
Data is at the center of all digital transformation projects and initiatives. The aim is to make better use of your organization’s data to help achieve operational goals. Some examples include:
- Optimising processes, including digitalizing processes and transitioning from paper to glass.
- Improving data-driven decision-making.
- Facilitating automated decision-making.
- Enhancing the visibility of your operations.
- Enabling predictive analytics and scenario modeling.
Digital transformation success relies on the integration of data. Depending on the project, different machines, devices, endpoints, applications, platforms, and systems must be integrated so data can be exchanged, accessed, and used.
The problem is that integrating data using traditional approaches is not as efficient and effective as it could be. UNS is the solution.
So, what is UNS?
In a sentence, UNS is an industrial architecture approach that simplifies and optimizes the integration of data through two core principles: centralization and standardization.
The Traditional Approach
Let’s start with an overview of the traditional architecture approach. The technology stack in manufacturing organizations has traditionally been based on the ISA-95 model. Here is our version of that model:
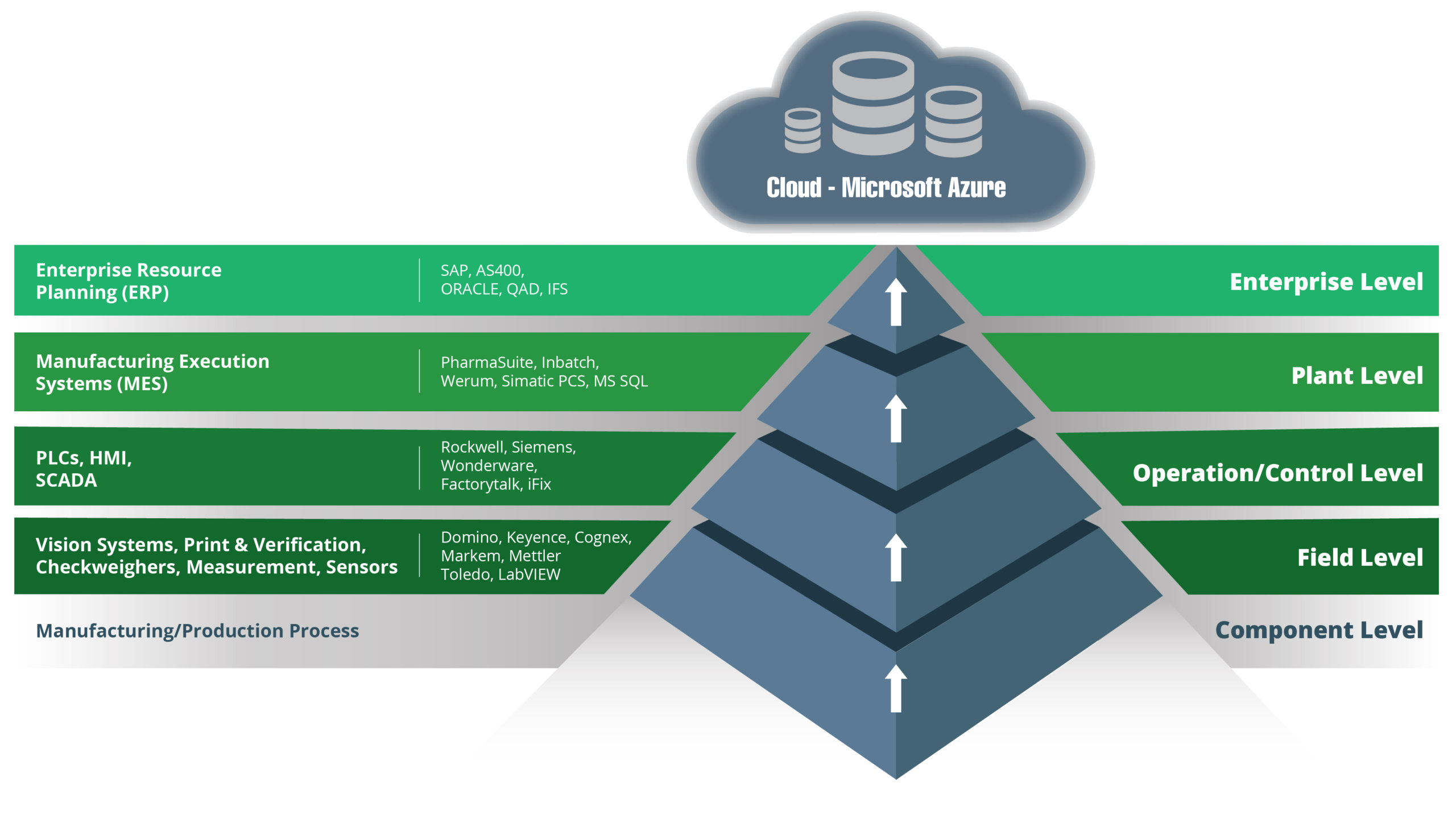
This is a model that has served manufacturers well for years, facilitating process improvements and enhancing automation. Technologies have evolved, however, as have business expectations and market conditions.
A data-driven approach to managing operations is today’s reality, and there is one key feature of the traditional model that makes that difficult to achieve. That feature is the hierarchical structure of the traditional model, where data can only move one layer at a time.
To integrate components in the stack using a hierarchical structure requires point-to-point connections and lots of them.
Limitations of the Traditional Model
To fully understand the importance of UNS, it is helpful to first look at the limitations of the traditional model described above. Those limitations include:
- Multiple point-to-point connections require engineering expertise while often adding layers of complexity.
- The creation and maintenance of multiple point-to-point connections is costly.
- It is expensive and difficult to scale using the traditional model.
- Data can be incomplete or inaccurate.
- Data formats differ across the various levels, so data must be converted, multiple times in some situations.
The UNS Architectural Approach Explained
In a UNS architecture, there is a single data environment that can be accessed by all components – systems, machines, applications, endpoints, etc:
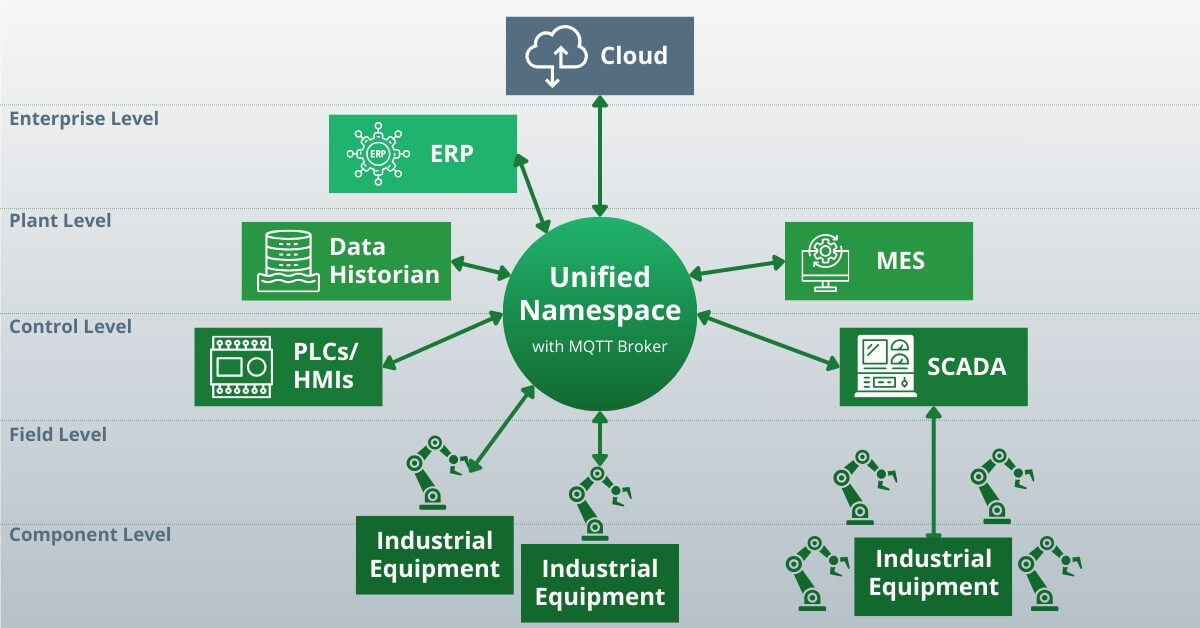
In other words, a UNS is a central repository for the information created and used by your manufacturing operations. It can exist anywhere, so long as it is accessible.
One of the key elements of a UNS is a naming convention. The naming convention standardizes the data and creates a single source of truth.
Another key element of a UNS is a communication interface. In manufacturing operations, this is typically an MQTT broker.
What is an MQTT Broker?
MQTT stands for message queuing telemetry transport. It is a messaging protocol designed to be lightweight and flexible, so it works in all types of environments and situations. This includes connections that have low bandwidth, high latency, or an unreliable network.
An MQTT broker is a central hub that allows the various components of the network (devices, SCADA systems, applications, etc) to publish data. Components can also subscribe to receive real-time updates on the data they need from other components.
This publisher/subscriber model of MQTT is beneficial to a UNS architecture as data is only exchanged between components that need it, speeding up the exchange and making the overall solution more flexible.
Benefits of a UNS Architecture
The advantages of using a UNS architecture include:
- Creates a central repository that contains standardized data
- Easy to scale
- Easy to integrate new components
- Reduces costs as only one communication interface is needed
- Improves operational agility as data on all components in the network is available in real-time
- Enhances oversight with real-time data, analytics, and dashboards
A UNS architecture will also enhance your digital transformation projects and initiatives, from paper-to-glass initiatives to process optimization to AI utilization and everything in between. It also helps to flatten the software stack in your organization, reducing digital transformation complexity – read our whitepaper on full stack OT (operational technology) platforms.
This blog is the first in a series we will be publishing on UNS. Upcoming blogs will explore in detail the platforms and technologies (including Ignition by Inductive Automation) that can deliver UNS. For more information on UNS architecture or to discuss your digital transformation requirements or objectives, please get in touch with us at SL Controls today.

