All sections of the life sciences sector understand the need to evolve operations using the cutting-edge technologies, processes, and best practices that come under the smart manufacturing umbrella. However, it’s important to take a structured approach, with a carefully developed and implemented smart manufacturing strategy.
In this blog, we’ll look at why it is important to develop an overarching smart manufacturing strategy, as well as providing an overview for creating one. The strategy overview that we present is relevant wherever you are on your smart manufacturing journey.
Change in the Life Sciences Sector and Why a Well-Structured Change Strategy is Important
The fact the life sciences sector is experiencing unprecedented change has been a common topic of discussion for some years now. The reality goes deeper than the concept of change, though, as change implies there will be an endpoint or conclusion.
However, the more likely scenario is that the life sciences sector has entered a period of ongoing change. New technologies are now developing at such a rapid pace that continuous evolution is now a reality and a necessity. Technologies like Microsoft’s HoloLens is a good example. It is now commonly used in many industrial applications, but nothing even close to it existed 10 years ago. Examples like this will become more commonplace over the coming years.
The ongoing changes that are taking place are not just the purview of technologies, either, as the life sciences sector is also experiencing changing customer expectations, markets, and products, all of which present opportunities. There are challenges too, of course, including skills, economic, business resilience, regulatory, and geopolitical challenges.
Smart manufacturing solutions help companies in the life sciences sector take advantage of the opportunities while addressing the challenges.
The Continuous State of Change – an Example
An example we can use to highlight the continuous state of change in the life sciences sector is the emerging trend of manufacturing operations needing to innovate at speed to keep up with cutting-edge product development breakthroughs.
A specific example is personalised pharmaceutical products that need to be produced as close to the patient as possible.
This means moving away from the mass production approach that has served the life sciences sector so well for decades (and other sectors for even longer). Instead of large manufacturing facilities producing and shipping products far and wide to reach the patients who need them, many personalised medicines will require batch-size-of-one manufacturing processes and, potentially, factory-in-a-box solutions where manufacturing capabilities, rather than the manufactured product, are brought to the patient.
Adopting a smart manufacturing approach is the only way to address the needs of today (productivity, competitiveness, quality, compliance, etc), as well as keeping up with the developments of the not-too-distant future (such as those in this example).
What is Smart Manufacturing?
It is helpful when developing a smart manufacturing strategy to look at what we mean by “smart manufacturing”. Some definitions include descriptions like the digitalisation of manufacturing processes. Automation is a key component, but it is only one element. Becoming a data-driven operation is also crucial.
However, it is often better to look at smart manufacturing through the lens of outcomes and objectives. Examples include:
- Improvements in key manufacturing metrics such as OEE and productivity.
- Improved resilience to deal with market challenges as well as enhanced agility to take advantage of commercial opportunities.
- Enhanced scaling capabilities while enabling production facilities to be more flexible, including in relation to producing different products on the same line.
- Creating connected operations, whether connected across different facilities, production lines within the same facility, or equipment on a single production line. It also involves connecting manufacturing operations with other business units and departments.
All the above objectives and outcomes can be achieved with a well-structured and implemented smart manufacturing strategy.
Smart Manufacturing Strategy Overview
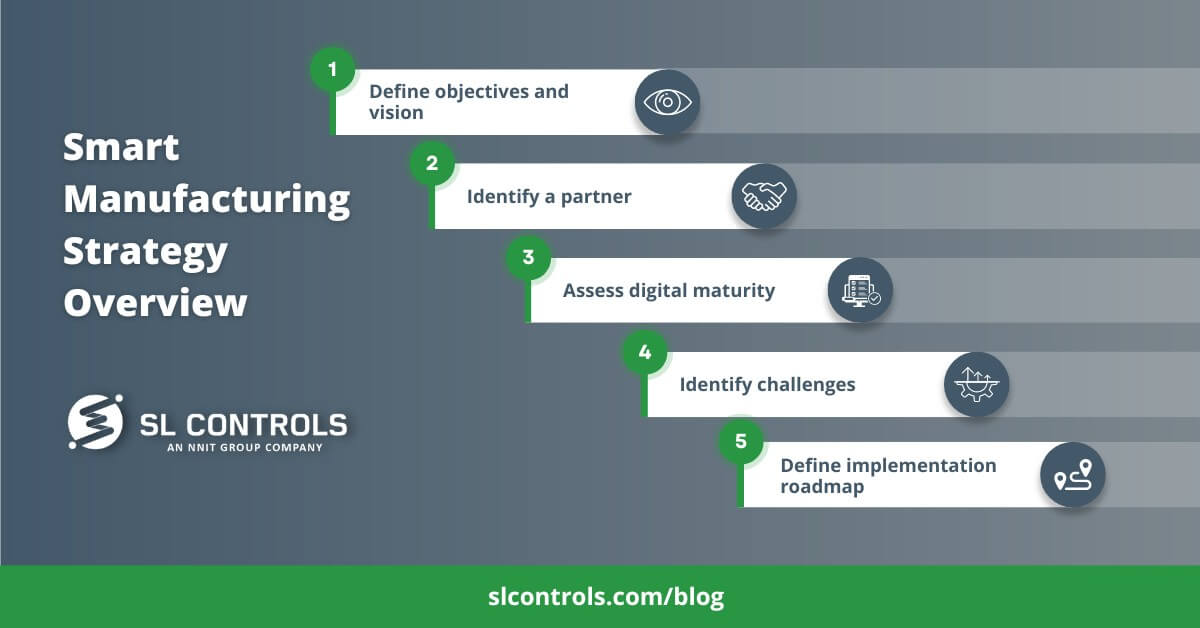
Step 1 – Define Objectives and Vision
The first step is to look at your production operations, wider business strategy, and corporate objectives. This includes:
- Immediate business challenges and risks
- Medium and long-term business goals
- Manufacturing and operational priorities
Step 2 – Identify a Partner
Getting the right partner is essential to help with both the planning and implementation of your smart manufacturing strategy. The qualities you should look for in a smart manufacturing partner include:
- Expertise in the life sciences sector as well as specific pharmaceutical and/or medical device industry experience.
- Broad range of technology expertise.
- A proven track record of delivering smart manufacturing projects in the pharmaceutical and medical device industries.
- Established expertise in the essential aspects of smart manufacturing projects, including change management, project management, equipment systems integration, and ongoing support.
Step 3 – Assess Digital Maturity
The roadmap to smart manufacturing success will depend on your existing situation. Therefore, assessing your current levels of digital maturity is essential. Elements to analyse include:
- OT (operational technology) and IT infrastructure
- Current processes and workflows
- Existing resources and skills, as well as resource and skills challenges
- Technology platforms, applications, and systems
- Production line equipment
Step 4 – Identify Challenges
Identifying the specific challenges faced by your organisation is also essential, as it allows the project management and implementation team to put in place mitigation measures and/or solutions. Challenges can be caused by a range of factors:
- Organisational
- Cultural
- Resources and skills
- Technology
- Financial
Step 5 – Define the Implementation Roadmap
This is the point where you decide on the next phase of development before implementing the project. Common steps include:
- Identify suitable project/s.
- Make sure your plans are in alignment with business objectives and adjacent projects.
- Create a business case and get organisational buy-in.
- Develop and implement a project implementation strategy, including technical and functional plans.
Taking the Next Steps
Delaying the next phase of your smart manufacturing journey will only set you further behind. The best approach is to start implementing the above strategy now to ensure your manufacturing operations evolve in step with the ongoing changes in the industry.
You don’t need to have all the answers, and you don’t even know what projects to undertake next. Looking at your business objectives and engaging a suitable partner will give you the answers you need while also ensuring you are on the path to success.





